amss/FDS_AMSS.c File Reference
Finite Difference Scheme for the Affine Morphological Scale Space. More...
#include <stdlib.h>#include <tiffio.h>#include <time.h>#include <math.h>#include "io_tiff_routine.h"

Go to the source code of this file.
Defines | |
| #define | FATAL(MSG) |
| #define | INFO(MSG) |
| #define | DEBUG(MSG) |
Functions | |
| static void | heat (float *ptr_out, float *ptr_in, size_t n_col, int i, int i_prev, int i_next, int j, int j_prev, int j_next, float dt) |
| Computes one iteration of Heat Equation. | |
| static void | amss (float *ptr_out, float *ptr_in, size_t n_row, size_t n_col, float dt, float t_g) |
| Computes one iteration of the Affine Morphological Scale Space. | |
| int | main (int argc, char *argv[]) |
| main function call | |
Detailed Description
Finite Difference Scheme for the Affine Morphological Scale Space.
- Version:
- 1.3
requirements:
- ANSI C compiler
- libtiff
compilation:
- type "gcc FDS_AMSS.c io_tiff_all.c -ltiff -o amss.out" to obtain the executable file
- type "amss.out" followed by the required arguments to run the executable file
usage: this programs requires 3 arguments written in the following order,
- argv[1] contains the normalized scale you want to reach
- argv[2] contains the name of the input file
- argv[3] contains the name of the output file
The normalized scale represents the scale 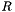 at which a circle with radius
at which a circle with radius 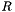 disappears. The number of iterations needed is linked to normalized scale and time step by the following formula:
disappears. The number of iterations needed is linked to normalized scale and time step by the following formula:
![\[ n_{iter}= \frac {3}{4 \cdot dt} R^{\frac{4}{3}} \]](form_1.png)
where 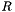 is the normalized scale,
is the normalized scale, 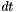 the time step and
the time step and 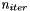 the number of iterations.
the number of iterations.
Definition in file FDS_AMSS.c.
Define Documentation
| #define DEBUG | ( | MSG | ) |
do {\ if (debug_flag)\ fprintf(stderr, __FILE__ ":%03i " MSG "\n", __LINE__);\ } while (0);
print a debug message, with detailed information
Definition at line 95 of file FDS_AMSS.c.
| #define FATAL | ( | MSG | ) |
do {\ fprintf(stderr, MSG "\n");\ abort();\ } while (0);
print a message and abort the execution
Definition at line 82 of file FDS_AMSS.c.
| #define INFO | ( | MSG | ) |
do {\ fprintf(stderr, MSG "\n");\ } while (0);
print an info message
Definition at line 89 of file FDS_AMSS.c.
Function Documentation
| static void amss | ( | float * | ptr_out, | |
| float * | ptr_in, | |||
| size_t | n_row, | |||
| size_t | n_col, | |||
| float | dt, | |||
| float | t_g | |||
| ) | [static] |
Computes one iteration of the Affine Morphological Scale Space.
This function applies a Finite Difference Scheme for Affine Curvature Motion
![\[ u_t=|Du|(curv(u))^{\frac{1}{3}}= (|Du|^3 curv(u))^{\frac{1}{3}} \]](form_7.png)
Similarly to MCM, when 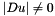 , we denote by
, we denote by 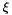 the direction orthogonal to
the direction orthogonal to 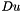 and by
and by 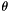 the angle between the
the angle between the 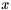 positive semiaxis and the gradient. Hence
positive semiaxis and the gradient. Hence
![\[ u_{\xi\xi}=D^2u(\xi,\xi)=D^2u\Bigl(\frac{Du^{\perp}}{|Du|},\frac{Du^{\perp}} {|Du|}\Bigr)= \frac{1}{|Du|^2}D^2u(Du^{\perp},Du^{\perp})= |Du|curv(u) \]](form_13.png)
and the continuous equation can be translated in this discrete version:
![\[ u_{n+1}(i,j)= u_n(i,j) + + \Delta t \cdot (|Du_n|^2 (u_{\xi\xi})_n)^{\frac{1}{3}}(i,j) \]](form_14.png)
As regards the numerical evaluation of 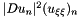 , we adopt a linear finite difference scheme based on a
, we adopt a linear finite difference scheme based on a 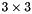 stencil.
stencil.
![\[ |Du_n|^2 (u_{\xi\xi})_n (i,j)=\frac{1}{\Delta x^2}( \hspace{0.3em} -4\eta_0 \cdot u_n(i,j)\hspace{0.3em} + \hspace{0.3em} \eta_1 \cdot (u_n(i,j+1) + u_n(i,j-1)) \hspace{0.3em} + \hspace{0.3em} \eta_2 \cdot (u_n(i+1,j) + u_n(i-1,j)) \hspace{0.3em} + \hspace{0.3em} \eta_3 \cdot (u_n(i-1,j-1) + u_n(i+1,j+1)) \hspace{0.3em} + \hspace{0.3em} \eta_4 \cdot (u_n(i-1,j+1) + u_n(i+1,j-1)) \hspace{0.3em}) \]](form_17.png)
which can be rewritten in a more synthetic form, using a discrete convolution with a variable kernel 
![\[ |Du_n|^2 (u_{\xi\xi})_n=\frac{1}{\Delta x^2}\cdot (B \star u_n) \quad \mbox{where} \quad B=\Biggl( \begin{array}{ccc} \eta_3(\theta) & \eta_2(\theta) & \eta_4(\theta) \\ \eta_1(\theta) & -4\eta_0(\theta) & \eta_1(\theta) \\ \eta_4(\theta) & \eta_2(\theta) & \eta_3(\theta) \end{array} \Biggr) \]](form_19.png)
We talk about 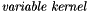 since the
since the 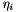 depend on the direction of
depend on the direction of 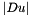 and can be calculated directly from the FDS of the partial derivatives
and can be calculated directly from the FDS of the partial derivatives 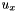 and
and 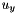 .
.
![\[ \begin{array}{l} u_x= \displaystyle \frac{2\cdot (u(i,j+1) - u(i,j-1)) + u(i-1,j+1) - u(i-1,j-1) + u(i+1,j+1) - u(i+1,j-1)} {8\Delta x}= \displaystyle \frac{s_x}{8\Delta x} \\ \\ u_y= \displaystyle \frac{2\cdot (u(i+1,j) - u(i-1,j)) + u(i+1,j+1) - u(i-1,j+1) + u(i+1,j-1) - u(i-1,j-1)} {8\Delta x}= \displaystyle \frac{s_y}{8\Delta x} \\ \end{array} \]](form_25.png)
where we have denoted respectively by 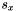 and
and 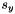 the algebric sums at the numerator of
the algebric sums at the numerator of 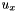 and
and 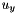 .
.
A very similar procedure is followed if we want to obtain an algorithm for MCM. The only difference is that for the Mean Curvature Motion we must discretize only 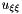 , which can be seen again as the result of a convolution with a discrete kernel
, which can be seen again as the result of a convolution with a discrete kernel 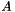 :
:
![\[ u_{\xi\xi_n}=\frac{1}{\Delta x^2}\cdot (A \star u_n) \quad \mbox{where} \quad A=\Biggl(\begin{array}{ccc} \lambda_3(\theta) & \lambda_2(\theta) & \lambda_4(\theta) \\ \lambda_1(\theta) & -4\lambda_0(\theta) & \lambda_1(\theta) \\ \lambda_4(\theta) & \lambda_2(\theta) & \lambda_3(\theta) \end{array} \Biggr) \]](form_30.png)
Thus the choice of the 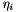 can be reduced to that of the
can be reduced to that of the 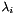 , since
, since 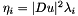 for
for 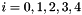 . Experiments have shown that if we take
. Experiments have shown that if we take 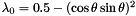 , i.e. the same value used in MCM, the best results as regards stability are achieved. Therefore the following formulas are actually adopted in the algorithm:
, i.e. the same value used in MCM, the best results as regards stability are achieved. Therefore the following formulas are actually adopted in the algorithm:
![\[ \begin{array}{l} \eta_0=\displaystyle\frac{1}{2} \cdot (u_x^2+u_y^2)-\frac{u_x^2 \cdot u_y^2} {u_x^2+u_y^2} \\ \\ \eta_1= 2\eta_0 - u_x^2 \\ \\ \eta_2= 2\eta_0 - u_y^2 \\ \\ \eta_3= -\eta_0 + \displaystyle \frac{1}{2} \cdot (u_x^2 + u_y^2 - u_x \cdot u_y) \\ \\ \eta_4= -\eta_0 + \displaystyle \frac{1}{2} \cdot (u_x^2 + u_y^2 + u_x \cdot u_y) \end{array} \]](form_35.png)
Remember that the array representing the image is examinated as a matrix, i.e. 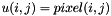 :
: 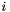 is the current row number and
is the current row number and 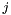 is the current column number. The infinitezimal
is the current column number. The infinitezimal 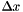 is the pixel width and is set to
is the pixel width and is set to 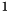 .
.
On the border, we symmetrize the image with respect to the axes 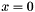 and
and 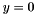 , i.e.
, i.e.
![\[ \begin{array}{l} u(-1,j) = u(0,j) \\ \\ u(n_{row},j) = u(n_{row}-1,j) \\ \\ u(i,-1) = u(i,0) \\ \\ u(i,n_{col}) = u(i,n_{col}-1) \end{array} \]](form_43.png)
From a theorical point of view, even if we divide by the gradient, there is no need to apply Heat Equation when 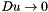 .
.
In fact 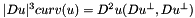 and, if
and, if 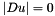 the Affine Morphological Scale Space is well defined. In addition even
the Affine Morphological Scale Space is well defined. In addition even 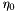 and consequently all the
and consequently all the 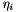 are well defined in the limit, since
are well defined in the limit, since 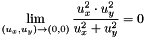 .
.
However rounding and approximation errors lead us to replace AMSS with Heat Equation when the gradient is below a threshold (experimentally set to 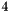 for the first iteration and then reduced to
for the first iteration and then reduced to 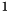 for the next ones).
for the next ones).
- Parameters:
-
[out] ptr_out pointer to the output array [in] ptr_in pointer to the input array [in] n_row number of rows [in] n_col number of columns [in] dt time step [in] t_g threshold for the gradient
Definition at line 301 of file FDS_AMSS.c.
| static void heat | ( | float * | ptr_out, | |
| float * | ptr_in, | |||
| size_t | n_col, | |||
| int | i, | |||
| int | i_prev, | |||
| int | i_next, | |||
| int | j, | |||
| int | j_prev, | |||
| int | j_next, | |||
| float | dt | |||
| ) | [static] |
Computes one iteration of Heat Equation.
This function applies the following Finite Difference Scheme for Heat Equation
![\[ u_{n+1} = u_n + dt \cdot \Delta u_n \]](form_4.png)
where the discrete laplacian 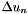 is given by
is given by
![\[ \Delta u_n = u_n(i+1,j) + u_n(i-1,j) + u_n(i,j+1) + u_n(i,j-1) - 4u_n(i,j) \]](form_6.png)
- Parameters:
-
[out] ptr_out pointer to the output array [in] ptr_in pointer to the input array [in] n_col number of columns i current row i_prev previous row i_next next row j current column j_prev previous column j_next next column [in] dt time step
Definition at line 135 of file FDS_AMSS.c.
| int main | ( | int | argc, | |
| char * | argv[] | |||
| ) |
main function call
The program reads an image.tiff given as input, applies a Finite Difference Scheme for the Affine Morphological Scale Space at renormalized scale 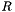 , writes the result as a new image.tiff and returns it as output.
, writes the result as a new image.tiff and returns it as output.
Definition at line 380 of file FDS_AMSS.c.
 1.6.3
1.6.3